Controls
Switches
Switch On/Off Light : Used to switch on/off the light.
Place Prism/Remove Prism : This switch used to place the prism on the prism table or remove prism from the prism table.
Slider
Slit focus : This slider used to focus the slit while looking through telescope.
Slit width : Using this slider, width of the slit can be adjusted.
Telescope: Using this slider one can move the telescope from its position.
Vernier Table: Vernier table can be rotate using this slider.
Fine Angle adjustment
Telescope: This is used to fine adjust the telescope.
Vernier Table: Using this slider , we can rotate fine angle.
Measurements
Here we get the zoomed view of vernier I and II by placing mouse pointer over it.
Procedure:
Preliminary adjustments:
Performing simulator
- Focus Telescope on distant object.
- When focus is correct, start button is activated. Then click Start button.
- Switch on the light by clicking Switch On Light button.
- Focus the slit using Slit focus slider.
- Adjust the slit width using Slit width slider.
- Coincide the slit with cross wire in the telescope.
Performing Real Lab:
- Turn the telescope towards the white wall or screen and looking through eye-piece, adjust its position till the cross wires are clearly seen.
- Turn the telescope towards window, focus the telescope to a long distant object.
- Place the telescope parallel to collimator.
- Place the collimator directed towards sodium vapor lamb. Switch on the lamp.
- Focus collimator slit using collimator focusing adjustment.
- Adjust the collimator slit width.
- Place prism table, note that the surface of the table is just below the level of telescope and collimator.
- Place spirit level on prism table. Adjust the base leveling screw till the bubble come at the centre of spirit level.
- Clamp the prism holder.
- Clamp the prism in which the sharp edge is facing towards the collimator, and base of the prism is at the clamp.
Least Count of Spectrometer
One main scale division (N) =................minute
Number of divisions on vernier (v) = ................
L.C = 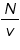 = .......................minute
= .......................minute
To determine the angle of the Prism:
Performing simulator
- Click Place Prism button.
- Place the edge of prism, pointed towards collimator.
- Move the telescope using Telescope slider up to see the slit on side. Make coincide the slit with the cross wire using fine angle adjusting slider. Then note the reading in the tabular coloumn.
- Move the telescope in the opposite direction and do the same.
- Find the difference between two angle ie 2θ. Hence, find the angle of prism i.e θ.
Performing Real Lab:
- Prism table is rotated in which the sharp edge of the prism is facing towards the collimator.
- Rotate the telescope in one direction up to which the reflected ray is shown through the telescope.
- Note corresponding main scale and vernier scale reading in both vernier (vernier I and vernier II).
- Rotate the telescope in opposite direction to view the reflected image of the collimator from the second face of prism.
- Note corresponding main scale and vernier scale reading in both vernier(vernier I and vernier II).
- Find the difference between two readings, i.e.θ
- Angle of prism, A=θ/2
.jpg)
Mean 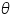 =..................Degrees
=..................Degrees
Angle of prism =..................Degrees
To determine the Cauchy's constants for the prism:
Performing Real Lab
The angle of the prism A and the angle of minimum deviation D for different wave length are determined. From this the refractive index n for these colours are calculated. Taking the value of λ from the mathematical table, the Cauchy’s constants A and B are calculated for different pairs of spectral colours using the equation.
The Cauchy’s constants can also be determined graphically. A graph is drawn with n along the y-axis and 1/λ2 along x-axis with zero as the origin for both axes. The graph is a straight line. The Y intercept gives A and the slope gives B.
Performing simulator

- Rotate the vernier table so as to fall the light from the collimator to one face of the prism and emerged through another face. (refer the given figure ).
- The emerged ray has different colors.
- Turn the telescope to each color, and note the readings for different colors.
- Remove the prism, hence note direct ray reading.
- Find the angle of minimum deviation for different color.(Say ,violet, blue, green, yellow).
- Find the refractive index for these colors. Using equation (3).
- Draw the graph with n along the y-axis and 1/λ2 along x-axis with zero as the origin for both axes.
,

Table (1): To calculate A and B.

Table (2): To find A and B graphicaly.
Graph:

Result:
| Cauchy's constants |
|
| |
A =…………………………… |
| |
B =…………………………… m2 |
| |
|




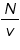 = .......................minute
= .......................minute.jpg)
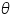 =..................Degrees
=..................Degrees


