
| . | . | |||||||
| . | Spectrometer: i-d curve |
. | ||||||
| . |
Controls
SwitchesSwitch On/Off Light : Used to switch on/off the light. Place Prism/Remove Prism : This switch used to place the prism on the prism table or remove prism from the prism table.
SliderSlit focus : This slider used to focus the slit while looking through telescope. Slit width : Using this slider, width of the slit can be adjusted. Telescope: Using this slider one can move the telescope from its position. Vernier Table: Vernier table can be rotate using this slider.
Fine Angle adjustmentTelescope: This is used to fine adjust the telescope. Vernier Table: Using this slider , we can rotate fine angle.
MeasurementsHere we get the zoomed view of vernier I and II by placing mouse pointer over it.
Procedure:
Preliminary adjustments:
Performing simulator
Performing Real Lab:
Least Count of Spectrometer
One main scale division (N) =................minute Number of divisions on vernier (v) = ................ L.C =
Procedure to find the angle of the prism
Click here to go to the procedure for finding angle of prism
To draw i-d curve and obtain angle of minimum deviation
Indirect way to set the incident angle (i) in the spectrometer apparatus
Consider ab is the incident ray of light on one face of the prism. i is the angle of incident and d is the angle of deviation. Basic idea to set the incident angle is the ‘angle of incident and angle of reflection is same’. There for reflected ray from the surface of the prism is at an angle 180-2*i from c.
Fig (1) : Schematic representation of setting incident angle
To find angle of deviation (d) corresponds to incident angle iPerforming simulator
Step 1: View the direct ray without the prism. Set the vernier and main scale in 0-0 in 0-180 position.
Step 2: For incident angle i ( say 30), rotate the Telescope to 180-2*i degrees in the anti-clock wise direction. (make sure the 0 line on the one of the vernier scale coincide with 120 in the main scale), see fig (2)
Step 3: Rotate the vernier table in the clockwise direction so as to get the reflected image of slit from one face of the prism. And make it coincide with cross wire of the telescope by the fine angle of vernier table, without rotating the telescope. (Refer figure below). Note the reading as θ. See Fig(3)
Step 4: Rotate the telescope in clock wise direction, without disturbing the vernier table, to find the emergent ray from other face of the prism. See fig(4)
Step 5: Make the slit coincide with the cross wire of telescope.
Step 6: Note down corresponding vernier 1 and vernier II reading. This reading is called refracted reading.
Step 7: to find the direct ray reading- remove the prism by clicking “remove prism” button.
Step 9: Note down vernier I and vernier II readings. This reading is called directed ray reading.
Step 10: place the prism and bring vernier and main scale in 0-0 in 0-180 position.
Step 11: Repeat the step from 1 to 10, for different incident angle, and tabulate the readings and find angle of deviation (d).
Step 12: Plot the graph between i and d, where i is in x-axis and d is in y-axis. And note down the minimum value of d ( which is the angle of minimum deviation - D )
Fig (6): i-d curve
Step 13: Using the equation 3, find out the refractive index of the prism.
Performing Real lab
Plot the graph between i and d, where i is in x-axis and d is in y-axis. From the graph, found the angle of minimum deviation.
Result:
Cite this Simulator: |
..... | ||||||
| ..... | ..... | |||||||
 |
Copyright @ 2024 Under the NME ICT initiative of MHRD |
 |

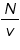 = .......................minute
= .......................minute



 Step 8: place the telescope in line with the collimator. (do not change vernier table position). See fig(5)
Step 8: place the telescope in line with the collimator. (do not change vernier table position). See fig(5)
