Procedure:
- Under the chemical content, select the tests- Hardness, Alkalinity or COD.
a. Determination of Hardness of Water Sample
- Select the titrant.
- Adjust the speed of the drops from the burette.
- Adjust the molarity of titrant.
- Select a definite volume of water sample.
- Choose the indicator & start the titration.
- When colour changes from wine red to blue click the "stop" button & note the volume of EDTA used.
- Then calculate the hardness of water sample in ppm using the equation as follows.
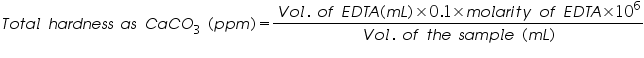
Observations And Calculations:
| No |
Vol. of the sample (mL) |
Burette Reading (mL) |
Vol.of EDTA (mL) |
| Initial |
Final |
| 1 |
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
|
|
|
|
Volume of EDTA used=..................mL.
Molarity of EDTA =..................M.
Volume of the water sample =..................mL.
Therefore the total hardness of the sample is = 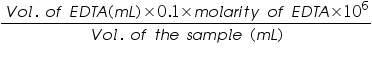 =.................ppm.
=.................ppm.
Result:
Total Hardness of the water sample = ..................ppm.
b. Determination of Alkalinity of Water Sample.
- Select the titrant.
- Select the normality.
- Adjust the speed of the drops from the burette.
- Select the titrate & choose a definite volume of the water sample.
- Select the indicator, phenolphthalein to get a pink colour.
- Stop titration when the solution becomes colourless & calculate phenolphthalein alkalinity (PA) as CaCO3 (mg/L) using the equation. Let A is the volume of titrant (mL) used in the titration (V1).
- Add methyl orange to the same flask & continue titration till the colour changes from yellow to orange. The total volume of titrant corresponds to total alkalinity (TA) as CaCO3 (mg/L). Let B is the total volume of titrant (mL) consumed with both the indicators (V2).
Observations and Calculations:
| No |
Vol. of the sample (mL) |
Burette Reading (mL) |
Vol.of HCl (mL) |
| Initial |
Final |
| 1 |
|
|
(A) |
|
| 2 |
|
|
(B) |
|
Volume of HCl corresponding to phenolphthalein end point (A)=..................mL.
Normality of acid =..................N
Volume of the water sample =..................mL.
Normality of water corresponding to phenolphthalein end point =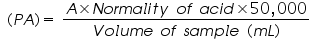 =..................ppm.
=..................ppm.
Volume of HCl corresponding to methyl orange end point (B)=..................mL.
Normality of acid =..................N
Volume of the water sample =..................mL.
Normality of water corresponding to methyl orange end point =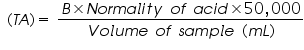 =..................ppm.
=..................ppm.
|
Result of Titration
|
OH alkalinity as CaCO3
|
CO3 alkalinity as CaCO3
|
HCO3 alkalinity as CaCO3
|
|
PA = 0
|
0
|
0
|
TA
|
|
PA < 1/2TA
|
0
|
2PA
|
TA - 2PA
|
|
PA = 1/2TA
|
0
|
2PA
|
0
|
|
PA > 1/2TA
|
2PA - TA
|
2(TA - PA)
|
0
|
|
PA = TA
|
TA
|
0
|
0
|
Results:
Alkalinity is due to............ =..............ppm.
c. Determination of COD of water sample
- Select the water sample.
- To reflux the contents in the RB flask click the "switch on mantle" button.
- Click "start titration" to titrate the contents.
- Select the normality of ferrous ammonium sulphate (FAS).
- Start titration & note the volume of titrant consumed when colour changes from bluish green to wine red. (Let the volume of titrant be V2 mL).
- Repeat the same with the blank (Let the volume of the titrant be V1mL).
- COD calculated using the equation.
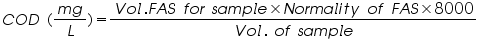
Observations And Calculations:
| Sample |
NO |
Vol. of sample (mL) |
Burette Reading (mL) |
Vol.of FAS (mL) |
| Initial |
Final |
| Sample |
1 |
20 |
0 |
|
|
| 2 |
20 |
0 |
|
|
| Blank |
1 |
20 |
0 |
|
|
| 2 |
20 |
0 |
|
|
Volume of FAS used= (V1-V2) =..................mL.
Normality of FAS =..................N.
Volume of the water sample =..................mL.
Therefore COD of the water sample = 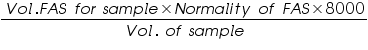 =..............ppm.
=..............ppm.
Result:
COD of water sample =....................ppm.
Points to Remember while Performing the Experiment in a Real Laboratory:
- Always wear lab coat and gloves when you are in the lab. When you enter the lab, switch on the exhaust fan and make sure that all the chemicals and reagents required for the experiment are available. If it is not available, prepare the reagents using the components for reagent preparation.
- Properly adjust the flame of the Bunsen burner. The proper flame is a small blue cone; it is not a large plume, nor is it orange.
- Make sure to clean all your working apparatus with chromic acid and distilled water and ensure that all the apparatus are free from water droplets while performing the experiment.
- Make sure to calibrate the electronic weigh balance before taking the measurements.
- Clean all glass wares with soap and distilled water. Once the experiment completed recap the reagent bottles. Switch off the light, exhaust fan and Gas cylinder before leaving the lab.
- Discard the used gloves in a waste bin.




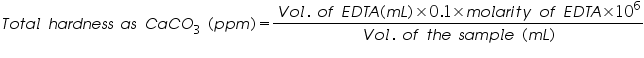
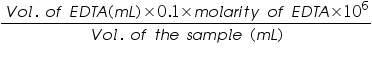 =.................ppm.
=.................ppm.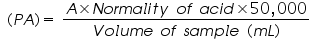 =..................ppm.
=..................ppm.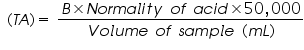 =..................ppm.
=..................ppm.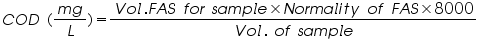
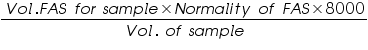 =..............ppm.
=..............ppm.