
| . | . | |||||||||||||||||
| . | Newton's Rings-Wavelength of light |
. | ||||||||||||||||
| . |
Performing Real Lab
After experimental arrangement, the glass plate is inclined at an angle 45° to the horizontal.This glass plate reflects light from the source vertically downloads and falls normally on the convex lens. Newton's rings are seen using a long focus microscope, focussed on the air fil. The cross-wire of the microscope is made tangential to the 20th ring on the left side of the centre. The readings of the main scale and vernier scale of the microscope are noted. The cross wire is adjusted to be tangential to the 18th, 16th, 14th, etc on the left and 2nd, 4th, 6th, etc on the right and readings are taken each time. From this the diameter of the ring is found out which is the difference between the readings on the left and right sides. The square of the diameter and hence Dn2 and D2n+m are found out. Then wavelength is calulated using equation. Performing the simulation:
The simulation virtualizes the Newton’s rings experiment. The user can view the effect of Newton’s rings formed when the medium changes. Select any one type of medium. Different ring pattern can be seen by changing the radius of curvature of the lens and wavelength of light source. . Components:
Start button, Light source, Filter, Microscope, Lens, Medium and Glass plate.
Help:
Variable region:
Measurement region:
Procedure:
Observations:
To find Least Count One main scale division = ............... cm Number of divisions on Vernier = ............... L.C = One main scale division/ Number of division on vernier=.................................
Calculation:
Mean value of D2m+p - D2m =.......cm2 =.............................nm
Result:
Wavelength of light from the given source is found to be = ..........nm
Cite this Simulator: |
..... | ||||||||||||||||
| ..... | ..... | |||||||||||||||||
 |
Copyright @ 2025 Under the NME ICT initiative of MHRD |
 |

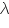 = (D2m+p - D2m)/4p
= (D2m+p - D2m)/4p